Interest rates have one of the strongest and most consistent relationships with the forex market. While currencies are influenced by many variables—such as geopolitics, economic growth, and market sentiment—interest rates remain the dominant fundamental driver of long-term currency movements.
In simple terms, capital tends to flow toward currencies offering the highest real interest rate, defined as the nominal interest rate minus inflation. Because of this, forex traders closely monitor central bank interest rates, and even more importantly, expectations of future rate changes, to anticipate moves in currency pairs.
In this article, I will explain how interest rates influence the forex market, how interest rate differentials work, how traders can forecast central bank decisions, and which interest rate–based forex trading strategies are commonly used by professional traders.
What Are Interest Rates and Why Do They Matter to Forex Traders?
When traders refer to “interest rates” in forex, they are typically talking about central bank policy rates. These rates are crucial because currencies tend to react not only to changes in interest rates themselves, but to changes in expectations about where rates are heading next.
Central banks use several monetary policy tools to influence interest rates, including:
- Open market operations: The buying and selling of securities to manage liquidity and influence rates
- The discount rate: The rate charged to commercial banks when borrowing directly from the central bank
The two primary objectives of central banks are to:
- Control inflation
- Maintain economic and currency stability
By adjusting interest rates and managing money supply, central banks attempt to strike a balance between economic growth and price stability.
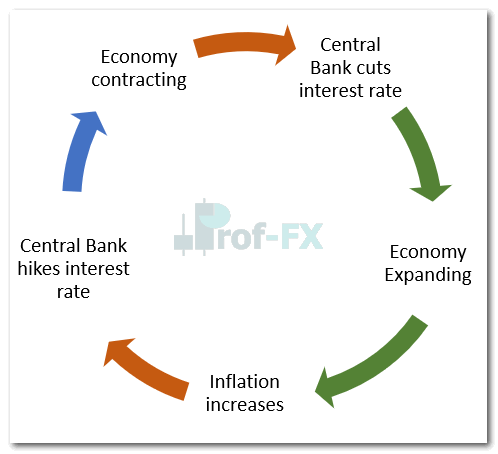
The Economic Cycle and the Role of Interest Rates
Economies naturally move through cycles of expansion and contraction. Central banks adjust interest rates in response to these phases to maintain economic balance.
During Economic Expansion
When GDP growth is positive, incomes rise and consumer spending increases. As demand grows, inflationary pressure builds. To prevent inflation from exceeding its target—commonly around 2% for most central banks—interest rates are increased.
Higher interest rates:
- Make borrowing more expensive
- Reduce spending and investment
- Help slow inflation
During Economic Contraction
When GDP growth turns negative, deflation becomes a risk. In response, central banks lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing, spending, and investment.
Lower interest rates:
- Encourage companies to invest
- Support job creation
- Help revive economic growth and inflation
This process creates a recurring cycle:
Understanding where an economy sits within this cycle gives forex traders valuable insight into future interest rate direction.
How Do Interest Rates Affect Currency Prices?
Interest rates influence currencies primarily through expectations. When the market’s expectations differ from actual central bank decisions, currencies often move sharply.
The table below illustrates common scenarios and their typical FX impact:
Market Expectations vs. Actual Outcome
- Rate hike expected → Rate held → Currency depreciation
- Rate cut expected → Rate held → Currency appreciation
- Rate held expected → Rate hike → Currency appreciation
- Rate held expected → Rate cut → Currency depreciation
This explains why currencies can fall even after a rate hike—if the market was expecting a larger increase.
Why Interest Rates Are So Important to Forex Trading
Consider a UK-based investor seeking a low-risk investment, such as government bonds. If US interest rates are rising, US bonds become more attractive, prompting investors to buy US dollars to access those higher yields.
As many investors do the same, demand for the US dollar increases, leading to currency appreciation. This flow of capital toward higher-yielding currencies is the core mechanism through which interest rates influence forex markets.
A clear example of this occurred when the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) unexpectedly cut interest rates from 2.00% to 1.75%. The market had anticipated no change, so the surprise rate cut caused the AUD/USD to depreciate sharply.
This demonstrates how unexpected interest rate decisions can trigger significant currency moves.
Understanding Forex Interest Rate Differentials
An interest rate differential is simply the difference between the interest rates of two countries in a currency pair.
If a trader expects the US Federal Reserve to raise rates unexpectedly, the trader may anticipate appreciation in the US dollar. To strengthen this view, the trader might buy USD against a currency with lower interest rates, increasing the divergence between the two currencies.
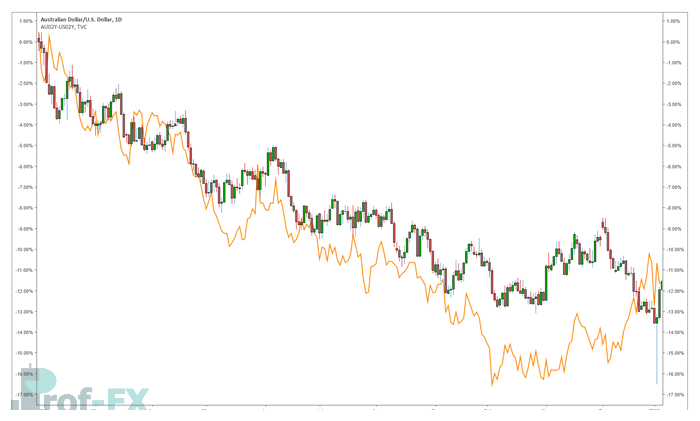
Interest rate differentials are strongly correlated with currency appreciation and depreciation. This relationship is often illustrated by comparing exchange rates with government bond yield spreads.
In the example below, the AUD/USD exchange rate is compared with the difference between two-year Australian and US government bond yields. As Australian yields fall relative to US yields, the AUD tends to weaken.
Interest Rate Differentials and Carry Trades
Interest rate differentials form the foundation of carry trades. In a carry trade, traders borrow in a low-interest-rate currency and invest in a higher-interest-rate currency, earning the yield difference.
While carry trades can be profitable during stable market conditions, they carry significant risk. If the higher-yielding currency depreciates sharply, exchange rate losses can outweigh the interest earned.
How Traders Forecast Central Bank Rates and FX Market Impact
One of the most widely used tools for forecasting US interest rates is Fed Funds Futures, traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). These contracts reflect market expectations for where the federal funds rate will be at contract expiration.
The market always has a forecast. A trader’s edge comes from anticipating changes in those expectations before they occur.
To do this, traders closely monitor what central bankers are focused on. Most central banks aim to be transparent, regularly communicating their concerns through speeches, meeting minutes, and policy statements.
Key economic data influencing rate decisions include:
- Inflation
- Employment and unemployment
- Economic growth
- Exchange rate stability
Key Economic Data That Influence Central Bank Interest Rate Decisions
Central banks do not change interest rates arbitrarily. Their decisions are driven by a consistent evaluation of key economic indicators that signal whether the economy is overheating, slowing down, or moving in line with policy objectives. For forex traders, understanding these data points is critical because interest rate expectations—rather than the decision itself—are what move currencies.
Below are the most important economic indicators that central banks closely monitor when setting interest rate policy.
Inflation: The Primary Driver of Interest Rate Policy
Inflation is the single most important factor influencing central bank interest rate decisions. Most major central banks—including the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, Bank of England, and Reserve Bank of Australia—operate under an inflation-targeting framework, typically aiming for around 2% annual inflation.
When inflation rises above target, central banks are more likely to increase interest rates to slow economic activity and reduce price pressures. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, which helps curb spending and cool inflation.
Conversely, when inflation falls below target or turns negative (deflation), central banks may cut interest rates to stimulate borrowing, spending, and investment.
For forex traders, inflation data such as CPI (Consumer Price Index) and PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures) are closely watched because they directly shape market expectations for future rate moves.
Employment and Unemployment: Measuring Economic Health
Labor market data plays a crucial role in interest rate decisions, especially for central banks with a dual mandate, such as the US Federal Reserve, which aims to achieve both price stability and maximum employment.
Strong employment growth, falling unemployment rates, and rising wages indicate a healthy economy. However, if the labor market becomes too tight, wage growth can fuel inflation, increasing the likelihood of interest rate hikes.
On the other hand, rising unemployment and weakening job creation signal economic slowdown. In such conditions, central banks may lower interest rates to support businesses, encourage hiring, and stabilize growth.
Key labor indicators forex traders monitor include:
- Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP)
- Unemployment rate
- Average hourly earnings
- Job vacancy and participation rates
These releases often cause sharp short-term volatility in currency markets due to their influence on interest rate expectations.
Economic Growth: GDP and Broader Activity Indicators
Economic growth, commonly measured by Gross Domestic Product (GDP), provides central banks with a broad view of how fast an economy is expanding or contracting.
When GDP growth is strong and sustained, it often leads to increased consumer spending and business investment, which can contribute to inflationary pressures. In such cases, central banks may lean toward tightening monetary policy by raising interest rates.
If economic growth slows or turns negative, central banks may respond with rate cuts or accommodative policies to prevent recession and support economic recovery.
Beyond GDP, central banks also track forward-looking indicators such as:
- Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI)
- Retail sales
- Industrial production
For forex traders, shifts in growth expectations often precede changes in interest rate outlooks, making these indicators valuable for medium- to long-term positioning.
Exchange Rate Stability and External Balance
While not always an explicit mandate, exchange rate stability is an important consideration for many central banks—particularly in open, trade-dependent economies.
A rapidly depreciating currency can:
- Increase imported inflation
- Reduce purchasing power
- Create financial instability
In response, central banks may raise interest rates to support the currency and restore investor confidence.
Conversely, an excessively strong currency can hurt exports and slow economic growth. In such cases, central banks may adopt a more dovish stance, including lower interest rates or accommodative guidance, to prevent the currency from appreciating too aggressively.
For forex traders, central bank concern over currency strength or weakness often appears in policy statements and speeches, offering valuable clues about future interest rate direction.
Why These Indicators Matter for Forex Traders
Understanding how inflation, employment, growth, and exchange rates influence central bank decisions allows forex traders to anticipate changes in interest rate expectations before they are fully priced into the market.
Rather than reacting to interest rate announcements alone, professional traders focus on:
- How incoming data shifts central bank bias
- Whether the data supports or contradicts current market expectations
- How those expectation changes may impact currency demand
This fundamental approach helps traders align themselves with longer-term currency trends driven by monetary policy.
An economic calendar is essential for tracking these releases. Traders who can anticipate how central banks will respond to incoming data often benefit from shifts in market expectations before official announcements.
This approach is rooted in fundamental analysis, which differs from technical analysis. Understanding both perspectives gives traders a more complete view of the market.
Key Forex Interest Rate Trading Strategies
Forex traders approach interest rate trading in several ways, depending on experience and risk tolerance.
Some traders choose to trade the news, entering positions immediately after an interest rate announcement. This approach requires speed, discipline, and an understanding of volatility.
More advanced traders focus on central bank communication and tone. Subtle changes in language during speeches or statements can shift market expectations well before actual rate changes occur.
Another common strategy is to wait for a pullback after a surprise rate decision. For example, if a central bank unexpectedly hikes rates, the currency may initially surge and then retrace. Traders may look to buy during the pullback, anticipating continuation in the direction of the rate-driven trend.
Key Concepts for Forex Traders
Several principles are essential when trading interest rates in the forex market:
- Market expectations matter more than the rate decision itself
- Larger interest rate differentials often support stronger currency trends
- Staying updated with economic data via an economic calendar is critical
Interest rates form the backbone of long-term currency valuation, making them indispensable for any trader seeking consistency in forex trading.
For further insight into how price reacts in the forex market, you may also find it useful to explore topics such as forex candlestick analysis, which complements both technical and fundamental approaches.