The Federal Reserve System, commonly referred to as the Fed, was established in 1913 by the United States Congress. Since then, it has become one of the most influential financial institutions in the world. For forex traders, understanding how the Fed operates is essential, as its policies and decisions have a direct and often immediate impact on the US Dollar (USD) and global currency markets.
This guide explores the structure, mandate, and influence of the Federal Reserve, while explaining how forex traders can approach trading around Fed monetary policy decisions.
What Is the Federal Reserve?
The Federal Reserve is the central bank of the United States, created to ensure a stable, flexible, and secure monetary and financial system. Its core responsibility is to formulate and implement monetary policy, while overseeing financial institutions and promoting economic stability.
At a high level, the Fed exists to serve the public interest by maintaining confidence in the financial system and supporting sustainable economic growth.
To achieve these objectives, the Federal Reserve carries out five key functions:
- Promoting maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates
- Reducing systemic risk to support overall financial stability
- Supervising and regulating financial institutions to ensure safety and soundness
- Maintaining the security and efficiency of payment and settlement systems
- Protecting consumers through regulation and supervision
Structure of the Federal Reserve System
The United States is divided into 12 Federal Reserve Districts, each served by its own regional Federal Reserve Bank. These regional banks operate independently in their respective districts but are overseen by the Federal Reserve Board of Governors, which is based in Washington, D.C.
The 12 Federal Reserve Banks are located in:
- Boston
- New York
- Philadelphia
- Cleveland
- Richmond
- Atlanta
- Chicago
- Louis
- Minneapolis
- Kansas City
- Dallas
- San Francisco
This decentralized structure allows the Fed to consider economic conditions across different regions of the country while maintaining a unified national monetary policy.
Who Owns the Federal Reserve?
The Federal Reserve has a unique hybrid ownership structure that blends both public and private elements, which often leads to confusion among traders and the general public. Unlike a typical central bank that is either fully government-owned or fully independent, the Fed was deliberately designed to balance independence, accountability, and regional representation.
At the core of the system is the Board of Governors, which is a federal government agency. Members of the Board are appointed by the President of the United States and confirmed by the Senate. They serve fixed terms and are tasked with overseeing the entire Federal Reserve System, shaping monetary policy, and ensuring that the Fed operates in the public interest. Because of this structure, the most important policy decisions—such as interest rate targets and regulatory oversight—are firmly rooted in public governance.
On the other side of the structure are the 12 regional Federal Reserve Banks, which are organized in a manner similar to private corporations. These Reserve Banks have their own balance sheets, boards of directors, and operational responsibilities within their respective districts. However, their corporate-like structure exists primarily to facilitate efficiency and regional economic insight rather than to generate profit.
Commercial banks that choose to become members of the Federal Reserve System are required to purchase stock in their regional Reserve Bank. This stock ownership is mandatory and highly restricted, meaning it cannot be sold, traded, or used as collateral. Member banks receive a limited, fixed dividend, which is not influenced by the profitability or performance of the Federal Reserve. Importantly, this stock does not confer voting power over monetary policy or control over Fed decision-making, unlike shares in a conventional private company.
Crucially for forex traders, monetary policy decisions remain fully independent of private commercial interests. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which sets interest rates and directs open market operations, operates independently of member banks. While regional Reserve Banks contribute economic research and market intelligence, ultimate policy authority lies with public officials whose mandate is to promote economic stability rather than private profit.
In practical terms, this hybrid model allows the Federal Reserve to:
- Maintain independence from short-term political pressure
- Incorporate real-world banking and economic conditions from across the country
- Preserve public accountability while ensuring operational efficiency
For traders, the key takeaway is that Fed policy is not driven by bank profits or shareholder incentives, but by macroeconomic objectives such as inflation control, employment, and financial stability. This institutional independence is one of the reasons Federal Reserve decisions carry significant credibility—and market impact—within global forex markets.
Who Is the Federal Reserve Chair?
The Chair of the Federal Reserve plays a central role in guiding US monetary policy and communicating policy decisions to the public and financial markets. The Chair also serves as the head of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), the body responsible for setting interest rate policy.
Because of this role, statements and press conferences by the Fed Chair are closely monitored by forex traders and frequently trigger volatility in USD-related currency pairs.
Accountability and Transparency of the Fed
Despite its independence, the Federal Reserve is accountable to both the public and the US Congress. This accountability is maintained through several mechanisms:
- Regular testimony by the Chair and senior officials before Congress
- Public release of FOMC statements after each policy meeting
- Publication of economic projections and meeting minutes
- Annual independent audits of financial statements
For traders, this transparency is valuable, as it provides insight into future policy direction and economic expectations.
Key Economic Mandates of the Federal Reserve
US monetary policy is the Fed’s core responsibility. Congress has defined three primary statutory objectives, often referred to as the dual mandate (with an additional interest rate objective):
1. Maximum Employment
The Fed aims to support conditions that foster job creation and low unemployment. When economic growth slows or unemployment rises, the Fed may adopt accommodative policies to stimulate activity.
2. Price Stability
The Fed defines price stability as long-term inflation around 2%. Maintaining stable prices helps preserve purchasing power and supports sustainable economic growth.
3. Moderate Long-Term Interest Rates
When inflation is controlled and employment is strong, long-term interest rates tend to remain at moderate levels, benefiting both consumers and businesses.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
Monetary policy in the United States is formulated and executed by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), one of the most influential policy-making bodies in global financial markets. For forex traders, understanding how the FOMC operates is essential, as its decisions often drive significant volatility in USD pairs across all time frames.
The FOMC meets eight scheduled times per year, with additional emergency meetings held when economic or financial conditions require urgent action. During these meetings, committee members assess a wide range of economic indicators, including inflation data, employment figures, GDP growth, financial market conditions, and global economic risks. The outcome of these deliberations determines the overall stance of U.S. monetary policy—whether it is accommodative, neutral, or restrictive.
At the heart of FOMC policy decisions is the setting of a target range for the federal funds rate. This rate represents the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to each other overnight. Although the Federal Reserve does not directly set the market rate itself, it exerts strong influence to ensure the effective rate trades within the announced target range. Changes in expectations surrounding this rate are among the most powerful drivers of short-term currency movements.
To influence the federal funds rate and broader financial conditions, the Federal Reserve relies on three primary monetary policy tools.
Open Market Operations (OMO)
Open market operations are the most frequently used and flexible tool of monetary policy. They involve the buying and selling of U.S. government securities in the open market.
When the Fed buys government bonds, it injects liquidity into the financial system by increasing the money supply. This action tends to push interest rates lower, stimulate borrowing, and support economic activity. From a forex perspective, such actions are generally viewed as USD-negative, especially if markets were expecting a tighter stance.
Conversely, when the Fed sells government bonds, it removes liquidity from the system, reducing the money supply. This typically leads to higher interest rates, tighter financial conditions, and can result in USD appreciation, particularly when combined with strong economic data.
Discount Rate
The discount rate is the interest rate charged to commercial banks when they borrow funds directly from the Federal Reserve through the discount window. While this facility is used less frequently than open market operations, changes to the discount rate serve as an important signal of policy intent.
A lower discount rate encourages banks to borrow more freely, increasing liquidity in the system and potentially lowering broader market interest rates. A higher discount rate has the opposite effect, discouraging borrowing and tightening financial conditions. For traders, adjustments to the discount rate often reinforce the broader message conveyed by FOMC statements and press conferences.
Reserve Requirements
Reserve requirements refer to the percentage of customer deposits that banks must hold in reserve, either as cash or on deposit with the Federal Reserve. By adjusting these requirements, the Fed can directly influence how much money banks are able to lend.
Higher reserve requirements restrict lending capacity, reduce money circulation, and tend to exert upward pressure on interest rates. Lower reserve requirements free up capital for lending, increase liquidity, and generally support economic expansion. Although changes to reserve requirements are relatively rare in modern monetary policy, they remain a powerful structural tool with significant long-term implications.
Why the FOMC Matters to Forex Traders
For forex traders, the importance of the FOMC extends beyond the actual interest rate decision. Forward guidance, economic projections, and the tone of the Fed Chair’s press conference often have an even greater impact on currency markets than the rate announcement itself.
Understanding how the FOMC uses its policy tools allows traders to better anticipate:
- Shifts in USD strength or weakness
- Periods of heightened volatility around FOMC meetings
- Medium- to long-term trends driven by interest rate differentials
In summary, the FOMC is not only the engine behind U.S. monetary policy, but also a central force shaping global capital flows—making it a critical institution for every forex trader to monitor closely.
How the Federal Funds Rate Affects the US Dollar
Interest rates are one of the most powerful drivers of currency value. Both actual rate changes and market expectations play a crucial role in determining the direction of the US Dollar.
In general:
- Higher interest rates tend to strengthen the USD, as they attract foreign capital
- Lower interest rates tend to weaken the USD, as returns on USD assets decline
Market Expectations vs. Outcomes
| Market Expectation | Actual Decision | Typical USD Reaction |
| Rate Hike | Rate Hold | USD depreciation |
| Rate Cut | Rate Hold | USD appreciation |
| Rate Hold | Rate Hike | USD appreciation |
| Rate Hold | Rate Cut | USD depreciation |
This explains why markets often move before official announcements—prices reflect expectations rather than just the final decision.
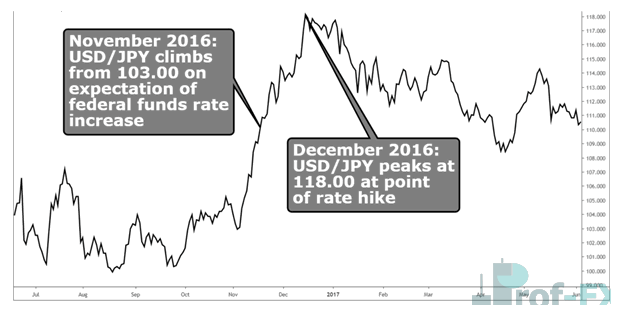
USD/JPY Example Around Fed Rate Decisions
The chart below illustrates how the US Dollar strengthened against the Japanese Yen ahead of a widely anticipated Fed rate hike. As expectations built, USD/JPY rallied leading into the announcement, highlighting how forward-looking forex markets can be.
How to Trade Fed Monetary Policy Decisions
Trading around Federal Reserve monetary policy decisions is one of the most challenging yet potentially rewarding aspects of forex trading. These events frequently trigger sharp price movements, increased volatility, and sudden shifts in market sentiment—especially in USD currency pairs. Successfully navigating these conditions requires thorough preparation, disciplined execution, and robust risk management, rather than impulsive trading during the announcement itself.
Professional traders typically focus on two key areas when preparing to trade Federal Reserve decisions.
1. Follow Federal Reserve Communications Closely
Federal Reserve communication is one of the most powerful drivers of market expectations. Traders should not limit their attention to the interest rate decision alone, as the market often reacts more strongly to the language and tone used by policymakers than to the headline outcome.
Key sources of Fed communication include FOMC statements, which are released immediately after each policy meeting. These statements outline the Fed’s assessment of economic conditions, inflation trends, employment data, and financial stability. Even subtle wording changes—such as shifts from “gradual” to “patient,” or from “monitoring” to “concerned”—can signal a meaningful change in policy direction and prompt swift reactions in the forex market.
FOMC meeting minutes, released several weeks after each meeting, provide deeper insight into internal discussions and differing viewpoints among committee members. Traders often analyze these minutes to gauge whether there is growing consensus toward tighter or looser policy. Markets may experience renewed volatility if the minutes reveal a more hawkish or dovish bias than previously expected.
Another crucial input comes from speeches and testimonies by Federal Reserve officials, including the Fed Chair, Vice Chair, and regional Fed presidents. These speeches often act as a form of forward guidance, shaping expectations ahead of future meetings. When multiple officials echo similar concerns—such as persistent inflation or weakening growth—markets tend to price in policy adjustments well before they occur.
For forex traders, the key skill is not just consuming this information, but interpreting it within the broader macroeconomic context. Understanding whether the Fed is leaning hawkish, dovish, or neutral allows traders to align their USD exposure with evolving policy expectations rather than reacting emotionally to short-term price spikes.
Practical Trading Insight
Many experienced traders avoid entering new positions during the exact moment of Fed announcements due to unpredictable spreads and slippage. Instead, they focus on:
- Positioning before the event based on expectations
- Trading after the market has digested the information and established direction
- Managing risk with wider stops or reduced position sizes
In essence, trading Fed decisions is less about predicting the outcome perfectly and more about understanding expectations, managing risk, and responding rationally to new information.
2. Monitor Market Expectations
When trading around Federal Reserve policy decisions, understanding market expectations is just as important—if not more important—than the actual outcome of the meeting. In many cases, the forex market reacts not to what the Fed does, but to whether its decision matches, exceeds, or falls short of expectations.
Traders closely monitor interest rate forecasts, analyst commentary, and futures market pricing—such as Fed Funds futures—to gauge how likely a rate hike, cut, or hold is perceived to be. These tools help reveal how much of a policy decision is already “priced in” by the market. When expectations are heavily skewed in one direction, even a neutral decision can trigger a sharp move if it diverges slightly from consensus.
For example, if markets are strongly positioned for a rate hike and the Fed instead signals a pause, the US Dollar may weaken sharply despite interest rates remaining unchanged. Conversely, a hawkish tone during a rate hold can still drive USD strength if traders had anticipated a more dovish outcome. This dynamic is why experienced traders focus on expectation versus reality, rather than the headline decision alone.
Because surprises can and do occur, especially during periods of economic uncertainty, traders must prioritize risk control over conviction. Even the most well-researched trade setup can fail if market sentiment shifts abruptly or liquidity conditions deteriorate during high-impact events.
To manage this risk effectively, traders should always:
- Use stop losses to protect capital against sudden adverse price movements
- Reduce position size during major announcements to limit exposure to volatility and slippage
- Stick to a clearly defined trading plan, outlining entry, exit, and risk parameters before the event occurs
Maintaining discipline during news-driven volatility is what separates consistent traders from emotional ones. No matter how confident a trade setup may appear, risk must always be controlled, as the forex market can react unpredictably when new information challenges existing assumptions.
Key Takeaways for Forex Traders
- The Federal Reserve is one of the most influential institutions in global forex markets
- FOMC meetings and interest rate decisions often create significant USD volatility
- Expectations matter just as much as actual policy decisions
- Proper preparation and risk management are essential when trading around Fed events
Understanding the Fed and its role in monetary policy gives traders valuable context when analyzing USD price movements and broader market trends.