Trading bias plays a critical role in helping traders make informed and structured decisions in the forex market. Whether you are a beginner just starting your trading journey or an experienced trader refining your edge, developing a clear trading bias allows you to approach the market with confidence and consistency.
In this presentation-style guide, we will walk through the essential foundations of trading bias, why it matters, and how traders can systematically develop it using proven technical tools. Specifically, this article will cover:
- What trading bias means in the context of forex trading
- Why every trader needs a clear trading bias
- How to develop trading bias using technical indicators
- Additional resources to strengthen your trading mindset
Understanding What Trading Bias Means
In forex trading, a trading bias refers to a trader’s directional expectation of the market. It is a structured perspective based on probability, where the trader believes one outcome—bullish or bearish—has a higher likelihood of occurring compared to alternative scenarios.
This bias is not based on emotion or guesswork. Instead, it is formed using technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both, supported by observable market behavior. Most commonly, trading bias aligns with market trends, identifying whether conditions favor buying (bullish) or selling (bearish).
By establishing a bias, traders gain clarity on which strategies are appropriate, how to engage the market, and when to avoid unnecessary trades.
Why Trading Bias Is Essential for Traders
Every trade involves multiple decisions, and without a defined bias, these decisions can quickly become overwhelming. Traders must decide:
- Which market to trade
- Whether to buy or sell
- When to enter the market
- How long to hold a position
- When to exit
- How much capital to risk
Without a trading bias, traders often hesitate, second-guess themselves, or act inconsistently. This is especially common among newer traders who struggle with balancing the potential for profit against the fear of loss.
Many novice traders rely heavily on recent trade outcomes, such as demo account performance, to guide future decisions. While some of these trades may appear profitable, they often involve unnecessary risk and lack long-term consistency. A trading bias helps anchor decisions to process and probability, rather than short-term emotional reactions.
Ultimately, trading bias provides structure. It simplifies decision-making and aligns every trade with a trader’s broader strategy and risk management rules.
Core Elements That Define a Trading Bias
To establish a reliable trading bias, traders must clearly define several key components:
Choosing the Right Market
Selecting a market is often the first challenge for beginners. Many traders gravitate toward popular currency pairs without considering whether those markets align with their strategy.
At Prof FX, traders can use the sentiment tool, which displays long and short retail positioning, to help identify potential opportunities. Beyond sentiment, traders may also select markets based on trend conditions, volatility, or macroeconomic relevance.
Some traders rely on fundamental analysis, examining political developments, central bank decisions, and macroeconomic data to determine which currency pairs to focus on.
Determining Trade Direction
Trade direction is closely linked to market trends. Depending on a trader’s time horizon, this could involve short-term, medium-term, or long-term trend analysis.
Once the trend is identified, the trading bias becomes clear:
- An uptrend supports a buy bias
- A downtrend supports a sell bias
This directional clarity prevents traders from fighting the market unnecessarily.
Defining Entry and Exit Points
Entries and exits are typically determined using technical indicators, price action, or a combination of both. Traders may use tools such as moving averages, support and resistance levels, or breakout patterns to identify optimal buy and sell points.
A trading bias does not dictate exact entries, but it ensures that all trades align with the dominant market direction.
Managing Trade Size
Trade size is a critical, yet often overlooked, component of a trading plan. Without proper position sizing, even a correct market bias can lead to poor results.
Trade size should always be adjusted according to account balance and risk tolerance. At Prof FX, we recommend that traders risk no more than 5% across all open positions, helping preserve capital and maintain long-term consistency.
Developing Trading Bias Using Technical Indicators
Technical indicators provide objective data that help traders reinforce their market bias. One of the most widely used tools for this purpose is the moving average.
Using the Moving Average to Define Bias
Moving averages are effective for identifying trend direction. A commonly used indicator is the 200-period simple moving average (SMA).
The concept is straightforward:
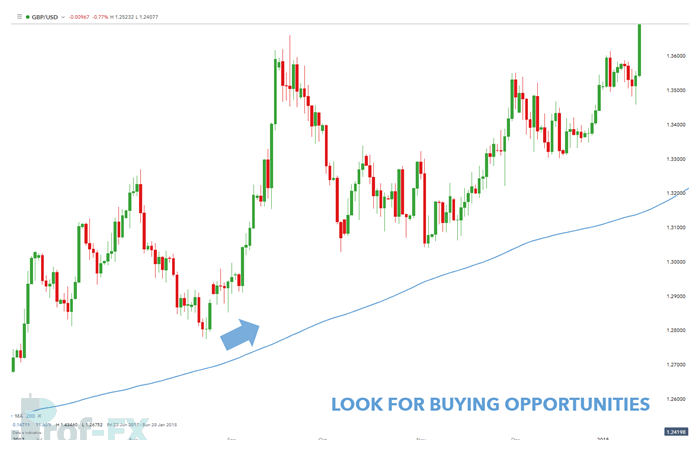
- If price is trading above the moving average, the bias is bullish
- If price is trading below the moving average, the bias is bearish
This method can be applied to any timeframe and is especially useful for trend-following strategies.
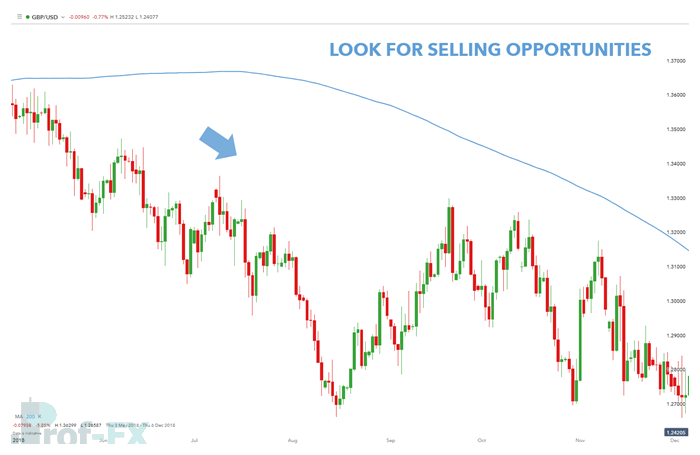
On the GBP/USD chart below, the 200-period moving average shows price trading well below the indicator. This suggests a bearish market environment, allowing traders—particularly short-term day traders—to focus on selling opportunities until price begins to recover and move back above the moving average.
Bearish Trading Bias Example
Bullish Trading Bias Example
Using Price Action to Establish Trading Bias
Price action is one of the most direct ways to identify market bias. By observing higher highs and higher lows, traders can confirm an uptrend and adopt a buying bias. Conversely, lower highs and lower lows indicate a downtrend and support a selling bias.
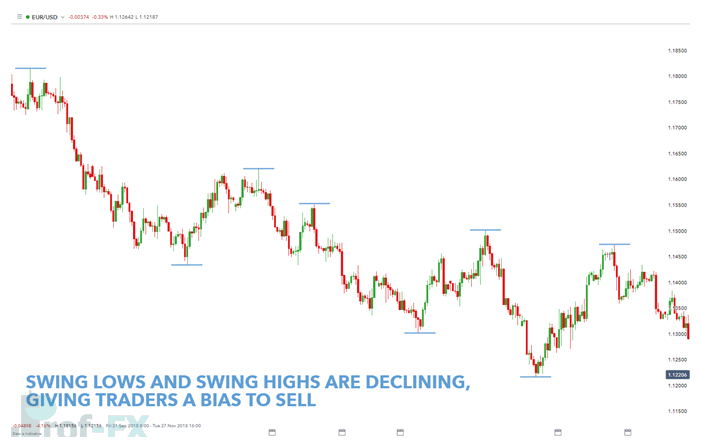
To apply this effectively, traders should review 200–300 historical periods on the chart. This approach works across nearly all trading strategies and timeframes.
EUR/USD Price Action Bias Example
The chart above shows a four-hour EUR/USD chart, covering nearly two months of price data. By reviewing approximately 300 candles, traders can clearly see price gradually moving toward lower lows. This consistent downward structure confirms a bearish trend and supports a selling bias.
Further Resources to Strengthen Your Trading Mindset
Developing a strong trading bias is closely tied to psychology and discipline. Traders are encouraged to explore Prof FX’s trading psychology article, which explains how mindset integrates with technical analysis.
Additionally, DFX analyst Paul Robinson hosts the Becoming a Better Trader webinar series, offering practical insights into consistent trading behavior.
Our research team has also analyzed over 30 million live trades, identifying the common traits shared by successful traders. Incorporating these behaviors into your strategy can provide a measurable edge in the forex market.
About Prof FX
Prof FX delivers timely forex news, technical analysis, and market insights focused on the trends shaping global currency markets. Our goal is to help traders develop clarity, discipline, and long-term consistency in their trading approach.