Effective Exit Methods Every Forex Trader Should Master
- Traditional Stop/Limit Orders Based on Support and Resistance
- Dynamic Trailing Stops Using Moving Averages
- Volatility-Adjusted Exits with the ATR (Average True Range) Indicator
In forex markets — whether trading major pairs such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, or commodities like XAU/USD (Gold) — mastering where to exit a trade is crucial. Even when traders use advanced platforms like MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), or TradingView, profits are only realized when closed properly.
Below are three proven exit techniques used by professional traders to secure gains and protect capital in both trending and volatile market conditions.
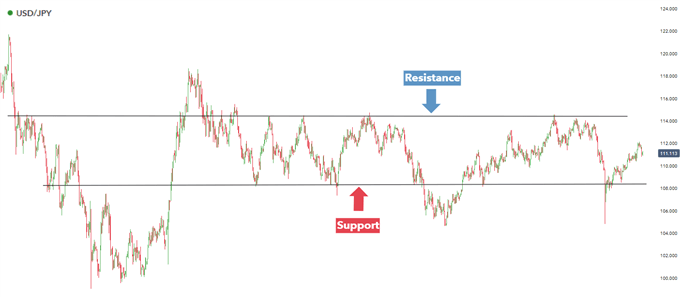
(H2) Strategy #1: Support & Resistance Based Stop/Limit Orders
Smart traders define stop-loss and take-profit levels the moment they open a position. This avoids emotional decision-making and keeps the trading plan objective — an essential skill in highly liquid markets like USD/JPY.
Industry data shows that successful traders typically follow a minimum 1:1 risk-to-reward ratio. To apply this:
- Identify key support/resistance zones using tools such as Fibonacci retracement, Price Action structures, or MACD divergence.
- Place a protective stop beyond invalidation levels.
- Set realistic profit targets based on technical confluence.
This ensures the market automatically provides your exit — win or lose — without requiring manual reaction.
Example: USD/JPY Using Strong Technical Levels
For long positions, traders may look for bullish candlestick patterns — such as a hammer or bullish engulfing — at support and confirm the entry with RSI or moving average alignment.
Stops sit just below support; take-profit sits near resistance.
For short trades, this logic simply reverses.
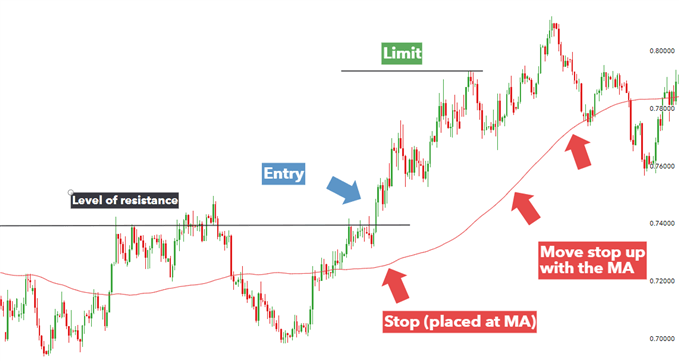
(H2) Strategy #2: Trailing Stops Using Moving Averages
Technical traders often rely on moving averages like the 100-day SMA or 50-day EMA to gauge directional bias in pairs such as AUD/USD or USD/CAD.
A moving average trailing stop dynamically follows price action — perfect for trending markets.
Example setup:
- Entry above 100-day SMA breakout (bullish trend)
- Stop initially placed 220 points away at the SMA
- Target at 440 points → a 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio
As price moves higher, the moving average rises too — meaning the stop should be manually trailed using your broker’s trade-management tool. This protects profit while allowing strong momentum trades to run.
This approach is especially favored by institutional trend followers and algorithmic traders.
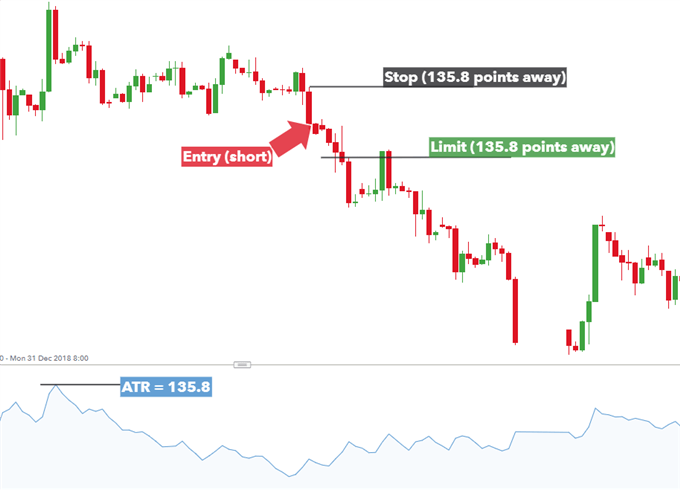
(H2) Strategy #3: ATR-Based Volatility Stops (Average True Range)
The ATR indicator measures average volatility over the previous 14 candles.
The method adapts well across timeframes — from scalping on M5 charts to swing trading on H4 or Daily charts.
Example: Brent Crude Oil with ATR peak at 135.8 pips
- Stop-loss = 135.8 pips from entry
- Take-profit = 135.8 pips (1:1 ratio)
However, as shown, a 1:1 exit resulted in an early closure despite favorable trend continuation.
For major forex pairs like EUR/JPY or NZD/USD, ATR-based stops are most effective when combined with higher reward multiples to avoid cutting winning trades too early.
ATR is widely adopted by professional traders and appears as a standard indicator across most ECN brokers’ platforms.
(H2) Final Takeaways: How Smart Traders Exit the Market
- Entries mean nothing without a structured exit strategy.
- New traders boost confidence using predefined rules on MT4/MT5 or TradingView.
- These exit strategies fit seamlessly with popular trading systems like:
- Breakout trading
- Price Action + RSI/MACD confluence
- Support & Resistance swing trading
- Breakout trading
To build a complete approach, explore our educational library on top forex trading strategies, trading psychology, money management, and platform optimization.
Prof FX continues to publish high-quality forex news, broker insights, technical analysis, and tutorials to support traders worldwide in volatile currency markets.