Gap trading is one of the most distinctive price action phenomena in financial markets. When used correctly, gaps can offer traders early insight into market sentiment, institutional positioning, and potential high-momentum opportunities. In this guide, we will explore what market gaps are, why they occur, the four major types of gaps, and how traders can build practical gap trading strategies while managing risk effectively.
This article is designed to help traders understand both the mechanics and psychology behind gaps, whether trading stocks, indices, or select forex instruments.
What Is a Gap in Trading?
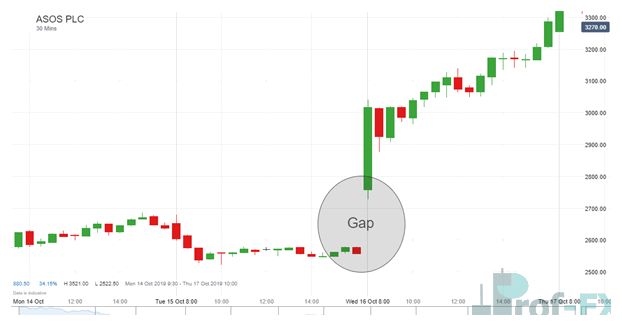
A gap refers to an area on a price chart where no trading activity has occurred. This happens when an asset opens at a price significantly higher or lower than its previous close, leaving an empty space on the chart between sessions.
In simple terms, the market “jumps” from one price level to another without trading in between.
Gaps are most commonly observed in stocks, indices, and futures, though they can also appear in forex markets during illiquid periods such as weekend openings or major fundamental announcements.
Why Do Market Gaps Occur?
The primary driver behind gaps is fundamental information entering the market when trading is paused or liquidity is thin.
Common catalysts include:
- Earnings reports and corporate guidance
- Economic data releases
- Central bank decisions
- Analyst upgrades or downgrades
- Mergers, acquisitions, or management changes
- Geopolitical or macroeconomic developments
For example, a stock may gap higher overnight after posting stronger-than-expected earnings, reflecting a sudden repricing of value by market participants.
In forex, gaps often occur:
- At the Sunday market open
- After unexpected central bank announcements
- During crisis-driven repricing (e.g., CHF, JPY, GBP events)
Gap Up vs Gap Down Explained
A gap up occurs when the opening price is above the previous session’s high, while a gap down occurs when the opening price is below the prior session’s low.
- Full gap up: Opening price exceeds the prior high
- Full gap down: Opening price drops below the prior low
Understanding direction is essential, but direction alone is not enough. Traders must also identify the type of gap, as this determines the most likely price behavior.
The Four Major Types of Market Gaps
1. Common Gaps: Noise, Not Opportunity
Common gaps appear frequently in quiet or low-volume conditions and are not associated with major trends or breakouts. These gaps tend to fill quickly and usually do not offer high-probability trading setups.
For most traders, common gaps are best ignored, as they often reflect short-term imbalance rather than meaningful sentiment.
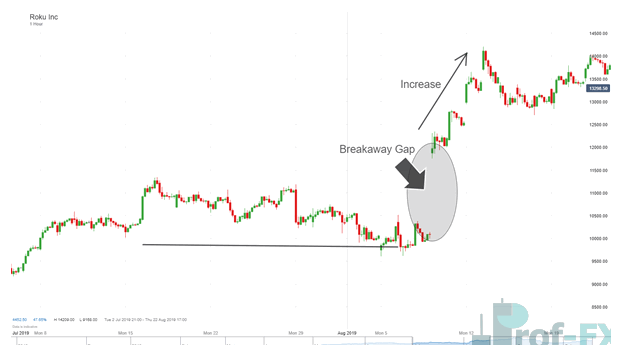
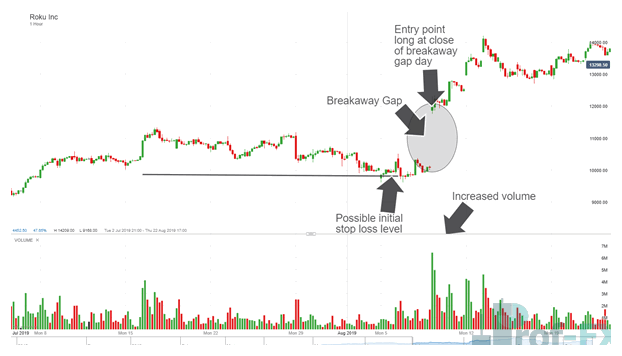
2. Breakaway Gaps: The Birth of a New Trend
Breakaway gaps occur when price gaps away from a consolidation zone or chart pattern, signaling the start of a new trend.
Key characteristics:
- Occur near support or resistance breaks
- Often accompanied by high volume
- Rarely fill immediately
Trading approach:
Traders may look to enter in the direction of the gap after confirmation, using the gap zone as a reference for stop placement. Conservative traders may wait for a pullback toward the gap area to reduce risk.
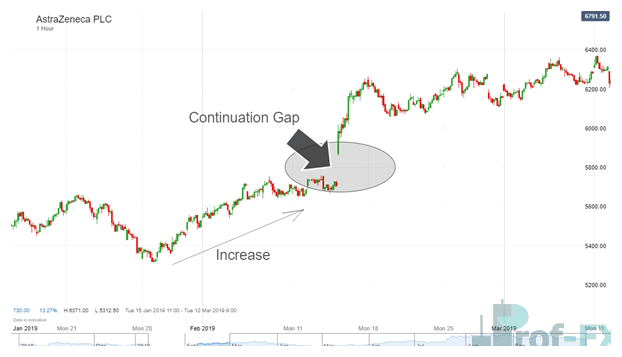
3. Continuation (Runaway) Gaps: Trend Acceleration
Continuation gaps appear mid-trend and signal increasing momentum in the prevailing direction.
These gaps reflect strong conviction, often driven by news that confirms existing sentiment.
Trading approach:
Trend-following traders may use continuation gaps to add to positions, placing stops just beyond the gap zone to protect against sudden reversals.
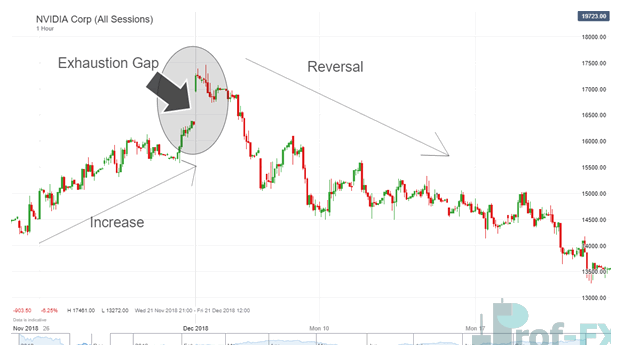
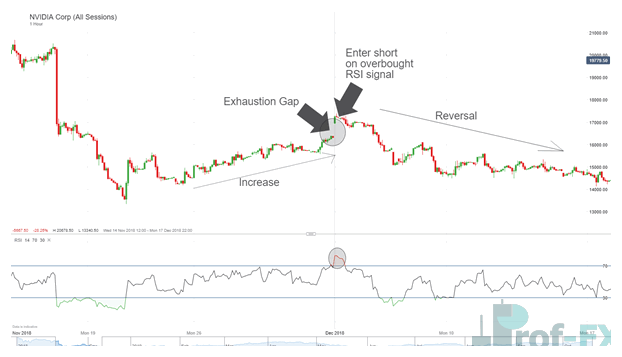
4. Exhaustion Gaps: The Final Push Before Reversal
Exhaustion gaps occur near the end of a mature trend and are often driven by emotional participation from latecomers.
This is where herd mentality and FOMO dominate price behavior. While price initially gaps in the trend direction, it soon loses momentum and reverses.
Trading approach:
Experienced traders monitor exhaustion gaps for reversal setups, often combining price action with indicators such as RSI divergence or volume contraction.
What Does It Mean When a Gap Is “Filled”?
A gap is considered filled when price returns to the level where the gap originated.
Gap fills often occur due to:
- Overreaction to news
- Lack of structural support or resistance
- Exhaustion of momentum
- Mean reversion dynamics
Not all gaps fill quickly. Breakaway and continuation gaps may remain open for extended periods, while exhaustion and common gaps are more likely to fill.
Gap Trading Strategies and Practical Techniques
Fading the Gap
“Fading the gap” involves trading against the direction of the gap, anticipating a gap fill.
This strategy works best when:
- The gap is driven by emotional or speculative behavior
- Volume declines after the open
- Price fails to continue in the gap direction
This approach requires discipline and strict risk control, as strong gaps can continue much further than expected.
Predicting a Gap Before It Happens
Some traders attempt to position themselves ahead of potential gaps, particularly around:
- Earnings announcements
- Central bank meetings
- High-impact macroeconomic events
While potentially rewarding, this approach carries higher risk and is best suited for traders with deep fundamental understanding and defined downside protection.
Using Indicators to Support Gap Trades
Indicators can help confirm gap strength or weakness:
- RSI to identify overbought or oversold conditions
- Exponential Moving Averages to assess trend alignment
- Volume analysis to validate breakaway gaps
Indicators should support, not replace, price action analysis.
Gap Trading Rules: Key Principles for Traders
- Always classify the gap before trading it
- Once a gap starts filling, it often continues
- Distinguish between institutional participation and retail emotion
- High volume supports continuation; low volume may warn of exhaustion
- Gaps involve low liquidity and high volatility, requiring conservative position sizing and disciplined stop-loss placement
Risk management is essential. Gap trading without predefined risk parameters can lead to outsized losses.
Final Thoughts on Trading Market Gaps
Gap trading offers a unique window into market psychology, sentiment shifts, and institutional behavior. Whether trading stocks, indices, or select forex pairs, understanding gaps can significantly improve a trader’s ability to read price action in context.
Like all strategies, gap trading works best when combined with:
- Trend analysis
- Price structure
- Volume confirmation
- Sound risk management
Used responsibly, gap analysis can become a powerful addition to any trader’s toolbox.