Risk management is one of the most critical components of a successful trading strategy, yet it is often underestimated—especially by new traders. While many focus primarily on finding profitable setups, professional traders understand that capital preservation is what keeps them in the game long enough to benefit from winning trades.
By applying proper risk management techniques, traders can significantly reduce the negative impact of losing positions on their overall portfolio, allowing consistency and longevity in trading performance.
In this guide, I will explain why risk management is essential, how traders can manage risk effectively, and which risk management tools are commonly used by professionals in the forex market.
What You Will Learn About Trading Risk Management
In this article, we will cover:
- Why risk management is essential for traders
- How to manage risk in trading using proven techniques
- Practical risk management tools used in forex trading
Why Is Trading Risk Management So Important?
Many traders enter the market with the primary goal of making money, but they often underestimate the potential for loss. Every trade carries risk, and without a structured risk management plan, even a few losing trades can cause significant damage to a trading account.
A trader who incorporates risk management into every trade can still benefit from favorable market moves while limiting downside exposure when the market moves against them. This balance is achieved through tools such as stop losses, take-profit orders, and diversification.
Traders who choose not to use stop losses often fall into the trap of holding losing positions too long, hoping the market will reverse. This behavior has consistently been identified as one of the most common and costly trading mistakes. Adopting the mindset and discipline seen in successful traders helps prevent this emotional decision-making.
How to Manage Risk in Trading: Professional Techniques and Best Practices
Below are six essential risk management techniques that traders of all experience levels should understand and apply consistently.
1) Determine Risk and Exposure Before Entering a Trade
Risk is inherent in every trade, which is why it must be defined before entering the market. A widely accepted guideline among professional traders is the 1% rule:
- Risk no more than 1% of account equity on a single trade
- Risk no more than 5% across all open positions at any time
For example, in a $10,000 trading account, risking 1% means the maximum loss on any single trade should not exceed $100. Once this amount is fixed, traders calculate position size based on how far the stop loss is placed.
This approach offers two major advantages:
- It protects account equity during losing streaks
- It preserves free margin, allowing traders to capitalize on new opportunities without being overexposed
2) Choosing the Optimal Stop Loss Level
Placing stop losses correctly is a core part of effective risk management. Stops should not be arbitrary; they must be based on market structure or volatility.
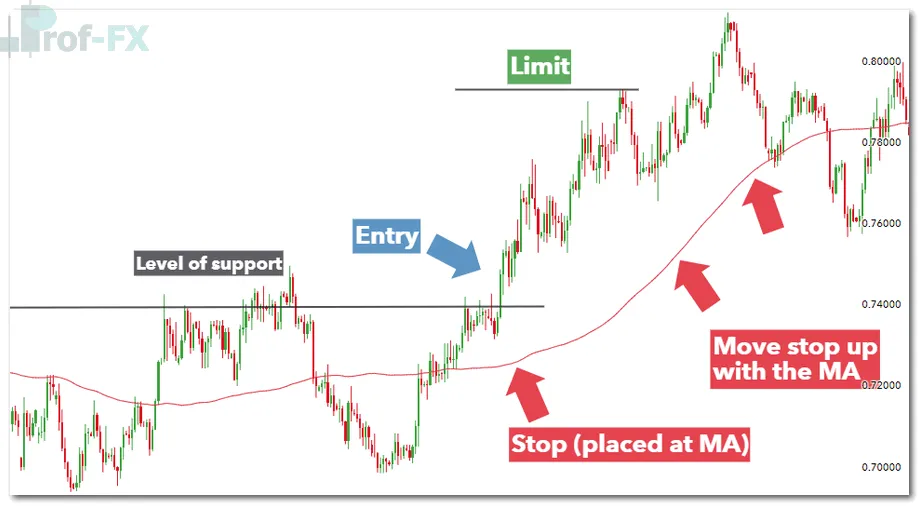
Using Moving Averages as Dynamic Stops
Moving averages can act as dynamic stop-loss levels:
- For long positions, stops are placed below the moving average
- For short positions, stops are placed above the moving average
This method allows the stop to adapt as price trends.
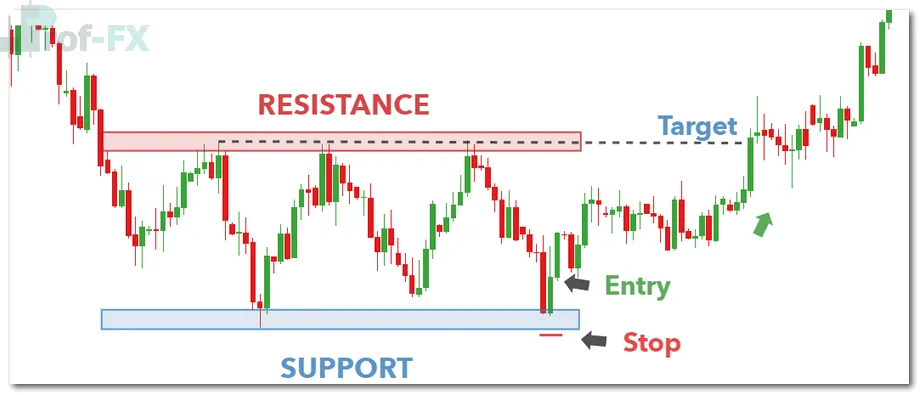
Using Support and Resistance Levels
Support and resistance are widely respected by market participants:
- Long positions: stops placed below support
- Short positions: stops placed above resistance
This approach gives trades room to develop while protecting against significant adverse moves.
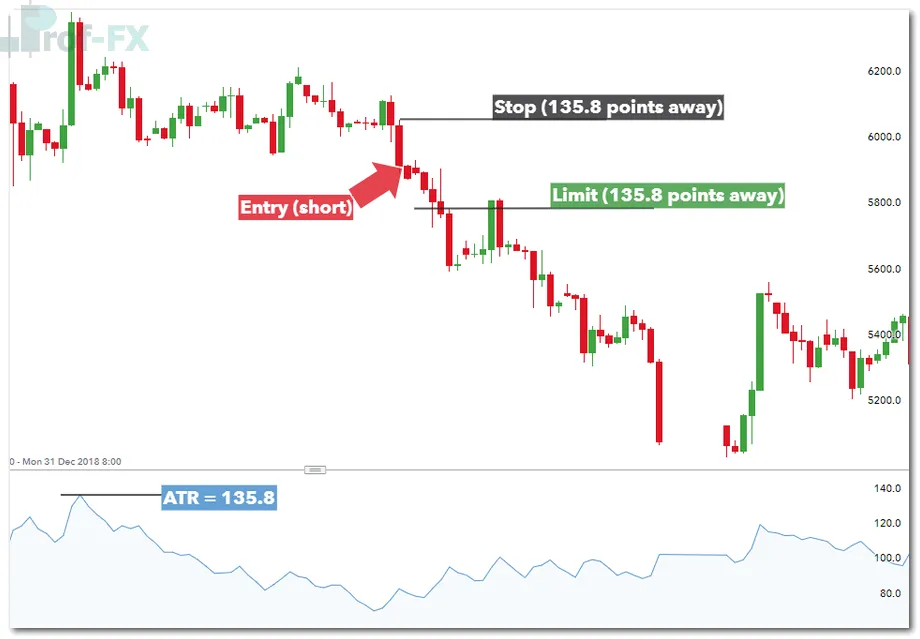
Using the Average True Range (ATR)
The Average True Range (ATR) measures market volatility and helps traders determine a realistic stop distance. By placing stops based on ATR values, traders avoid being stopped out by normal price fluctuations.
A conservative approach involves using the maximum recent ATR reading to set the stop distance.
Advanced Tip:
Instead of using a fixed stop, traders may apply a trailing stop. This allows the stop loss to move in favor of the trade while maintaining the original risk distance, helping to lock in profits as the market trends.
3) Diversify Your Portfolio: Lower Correlation Means Lower Risk
Even when risking only 1% per trade, portfolio risk can increase if positions are highly correlated.
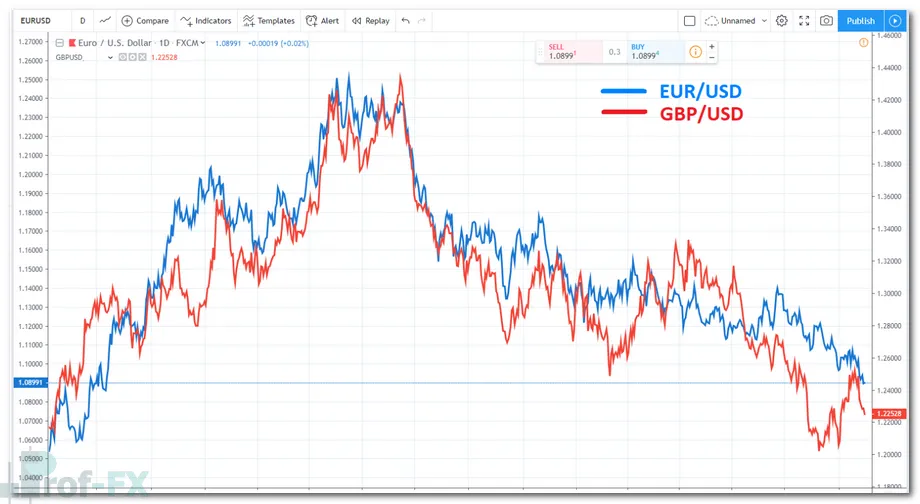
For example, EUR/USD and GBP/USD tend to move in the same direction due to their shared exposure to the US Dollar. When both positions move against the trader, losses can compound quickly.
Understanding correlations allows traders to build a diversified portfolio, reducing overall exposure and smoothing equity curves over time.
4) Keep Risk Consistent and Control Trading Emotions
After a series of winning trades, traders may feel tempted to increase position sizes. This behavior, driven by greed, is one of the fastest ways to erode capital.
Professional traders maintain consistent risk parameters, even during winning streaks. While adding to winning positions can be acceptable for experienced traders, risk must always remain within predefined limits.
Fear and greed are natural emotions, but learning how to manage them is essential for long-term success.
5) Maintain a Positive Risk-to-Reward Ratio
A positive risk-to-reward ratio is fundamental to sustainable trading performance. It measures how much a trader is willing to risk compared to the potential reward.
For example:
- A 1:2 risk-to-reward ratio means risking 1 pip to gain 2 pips
With this structure, traders can remain profitable even if they win only 50% of their trades. Research from the Traits of Successful Traders study shows that traders who consistently apply positive risk-to-reward ratios tend to outperform those who do not.
Advanced Tip:
Using a two-lot system can help manage trades more effectively. Half the position is closed midway to the target, while the remaining position is moved to break-even. This allows traders to secure partial profits while leaving a risk-free position open.
Trading Risk Management Tools Every Trader Should Know
Risk management tools are not optional features in trading platforms—they are core defensive mechanisms designed to protect capital and control downside risk. Understanding how each tool works, along with its advantages and limitations, allows traders to select the right protection for different market conditions.
Below are the three most commonly used risk management tools in forex trading, explained in practical terms.
1) Normal Stop Loss
A normal stop loss is the most basic and widely used risk management tool offered by forex brokers. It instructs the trading platform to close a position once price reaches a predetermined level, thereby limiting the maximum loss on a trade.
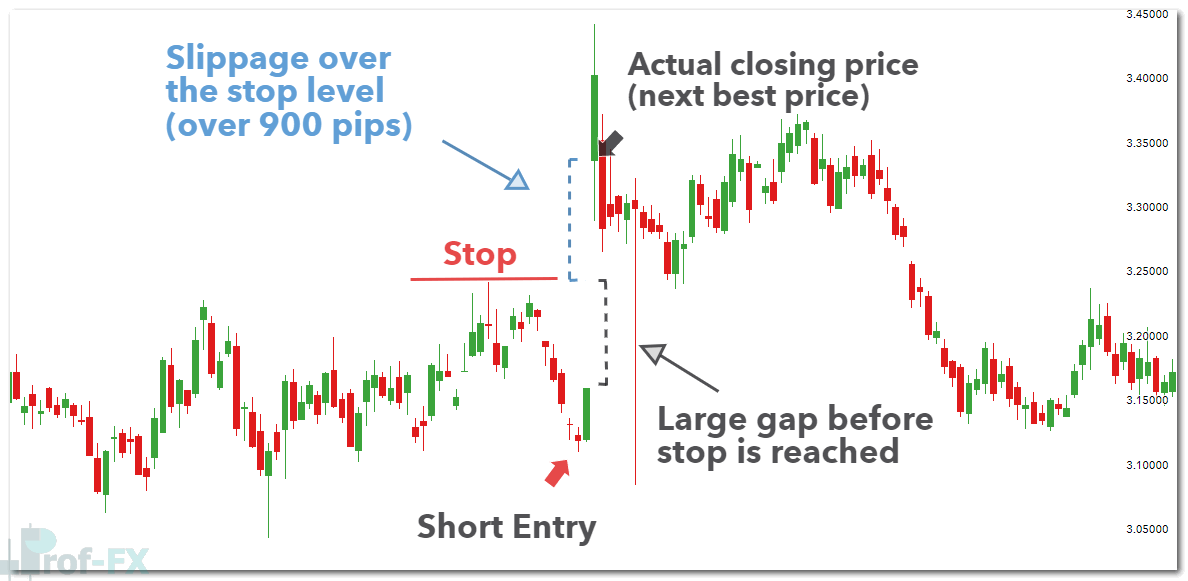
In stable or low-volatility market conditions, normal stop losses are generally effective and execute close to the intended price. However, during periods of heightened volatility—such as major economic releases, central bank announcements, or unexpected geopolitical events—normal stop losses can be vulnerable to slippage.
Slippage occurs when the market moves too quickly or gaps through the stop level, causing the trade to be closed at the next available price, which may be significantly worse than anticipated. This is especially common in:
- Thinly traded markets
- Sudden news-driven moves
- Weekend price gaps
Because of this, normal stop losses are best suited for:
- Range-bound markets
- Trades held during normal market hours
- Conditions where liquidity is stable
Example of slippage affecting a normal stop loss during volatile price movement
2) Guaranteed Stop Loss
A guaranteed stop loss provides an added layer of protection by ensuring that the trade is closed exactly at the specified stop level, regardless of market volatility or price gaps.
Even if the market gaps past the stop price, the broker absorbs the difference and honors the guaranteed level. This makes guaranteed stops particularly valuable during:
- High-impact economic news releases
- Earnings announcements
- Weekend exposure or overnight positions
- Extremely volatile market environments
The trade-off for this protection is cost. Brokers typically charge a small premium or percentage fee to use guaranteed stop losses. While this may slightly reduce profitability, many professional traders view it as an insurance cost—a price worth paying to eliminate catastrophic risk.
Guaranteed stops are especially useful for:
- New traders who prioritize capital protection
- Traders holding positions through major risk events
- Accounts with limited tolerance for drawdowns
3) Trailing Stop Loss
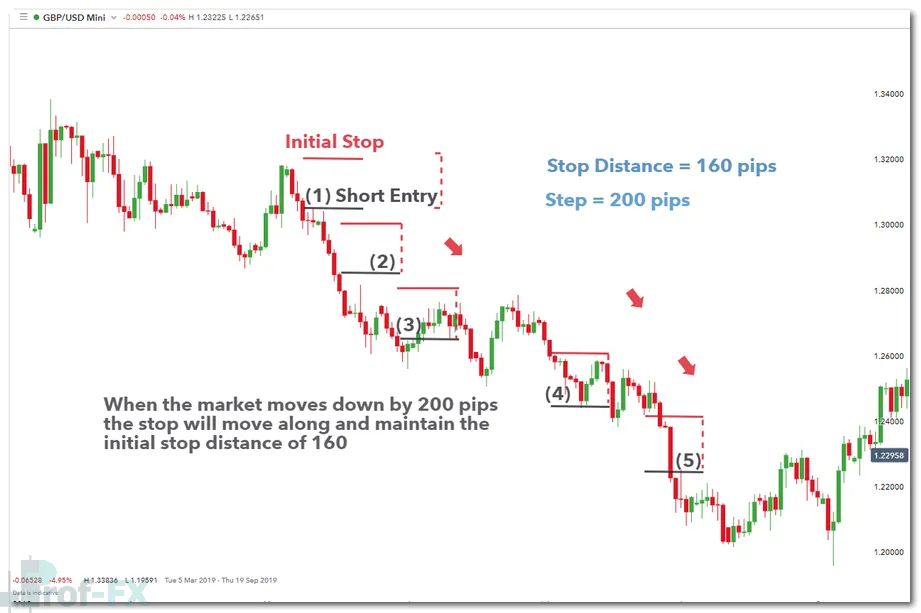
A trailing stop loss is a dynamic risk management tool that adjusts automatically as price moves in the trader’s favor, while maintaining the original stop distance set at the start of the trade.
For example, if a trader enters a position with a 100-pip trailing stop and price moves 50 pips in favor, the stop remains unchanged. Once price moves 100 pips in favor, the stop advances to the entry level. From that point onward, the stop continues to trail the price, locking in profits while allowing the trade room to develop.
Trailing stops are particularly effective in:
- Trending markets
- Momentum-based strategies
- Trades where traders want to reduce emotional involvement
By automating stop adjustments, trailing stops help traders:
- Protect unrealized profits
- Avoid premature exits due to fear
- Stay disciplined during extended trends
Example of a trailing stop following price movement in a trending market
Choosing the Right Stop Loss Tool
Each stop loss type serves a different purpose:
- Normal stop losses are suitable for routine trades in calm markets
- Guaranteed stops offer maximum protection during high-risk periods
- Trailing stops help maximize gains in trending conditions
Professional traders often combine these tools strategically, selecting the one that best fits the market environment, trade duration, and risk tolerance.
Final Insight for Traders
Risk management tools do not prevent losses—they define and control them. By understanding how stop losses behave under different market conditions, traders gain greater confidence and consistency in their execution.
Used correctly, these tools transform risk from an uncontrollable threat into a manageable component of a professional trading strategy.
Final Thoughts on Trading Risk Management
Risk management is not about avoiding losses—it is about controlling them. When applied consistently, these techniques allow traders to survive drawdowns, stay emotionally disciplined, and benefit from favorable market conditions over time.
Professional trading success is built on:
- Defined risk
- Consistent execution
- Emotional control
- Long-term thinking
Further Reading to Improve Your Risk Management Skills
- How leverage, stops, and risk-to-reward ratios fit into professional trading
- Risk management rules for scalpers
- Risk management strategies for day traders
Prof FX provides forex news and technical analysis on the trends that influence the global currency markets.