Understanding Employment as a Core Driver of Economic Performance
Employment is widely recognized as one of the most important indicators of economic strength. In economics, it functions as a key driver of national growth, consumer activity, and overall financial stability. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), unemployment refers to “people of working age who are without work, available for work, and actively seeking employment.”
This definition helps distinguish between two major groups in the labor market:
- Employed: Individuals currently holding jobs.
- Unemployed: Individuals not working but actively searching for employment.
While the unemployment rate is not a flawless metric, it remains a central component of fundamental analysis, similar to how market participants monitor supply and demand dynamics. Since changes in employment influence consumer spending, production capacity, and overall economic momentum, employment data is closely tied to Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Inflation—three pillars of macroeconomic policy objectives.
In the world of forex, employment-related releases rank among the most influential events on the economic calendar, frequently shaping central bank decisions and market sentiment.
(FX traders can follow scheduled central bank announcements through the central bank calendar.)
How Unemployment Influences Economic Policy
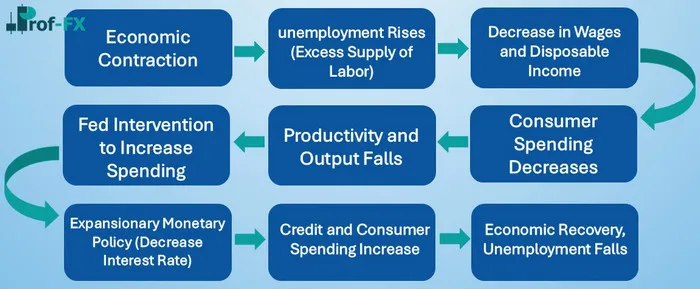
In the United States, the Federal Reserve (The Fed) relies heavily on employment statistics when adjusting monetary policy. When unemployment levels rise, it signals weakening economic momentum. In response, the Fed may adopt expansionary monetary policy—typically through lowering interest rates.
Why? Lower rates reduce borrowing costs, encourage spending and investment, and stimulate business growth. This creates a multiplier effect that supports economic recovery.
Below is a simplified illustration of how expansionary policy supports job creation and output growth:
When Employment Drops Too Low: The Connection Between Jobs and Inflation
While strong employment figures demonstrate economic strength, extremely low unemployment levels can trigger additional concerns—namely inflationary pressure.
Here’s how the mechanism typically works:
- Fewer unemployed workers means labor becomes scarce.
- Businesses compete for limited workers, raising wages to attract talent.
- Higher wages increase production costs and purchasing power.
- Result: Inflation, particularly wage-driven inflation.
Although low unemployment is positive, accelerating inflation is often viewed as a greater threat. This is why central banks, including the Fed, may shift to tightening monetary policy – raising interest rates – to keep price stability in check and prevent negative real rates or uncontrolled inflation.
In the U.S., traders monitor this wage-inflation dynamic through Average Hourly Earnings (AHE), a key component of the Non-Farm Payrolls report.
Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP): The Most Influential Employment Report in Forex Trading
The Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) report, published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) on the first Friday of every month at 08:30 EST, is one of the most important economic indicators globally. For forex traders, it is a direct barometer of U.S. economic health and a major driver of USD volatility.
Why Markets Care About NFP
- It provides early insights into economic conditions for the most recent month.
- It excludes sectors such as agriculture, private household workers, unpaid family workers, and volunteers—focusing instead on core industries that reflect real economic activity.
- It often undergoes revisions, meaning previous months’ data may be updated to reflect more accurate conditions.
The report is built from the Current Employment Statistics (CES) survey involving:
- 141,000 businesses and government agencies
- 486,000 individual worksites
- Covering about 80% of the U.S. workforce
Sectors included:
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Goods-producing industries
Because NFP is released alongside the Unemployment Rate and Average Hourly Earnings, the combined impact often sets the tone for market expectations—especially under the Federal Reserve’s close monitoring.
Economic Calendar and Monitoring Employment Reports
Staying informed about employment announcements—especially high-impact releases like Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP), Unemployment Rate, and Average Hourly Earnings (AHE)—is crucial for traders who want to anticipate market volatility and position themselves strategically. The economic calendar serves as a central tool for tracking these events, offering scheduled release dates, expected forecasts, previous data, and impact ratings that help traders prepare for potential market movements.
A detailed economic calendar helps traders understand when significant volatility may emerge, especially in USD-paired currency pairs such as EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, and XAU/USD (Gold). Because the U.S. dollar is the world’s primary reserve currency and a dominant safe-haven asset, employment data from the United States often sends ripples across global markets—from forex and commodities to equities and government bonds.
Why Employment Data on the Economic Calendar Matters to Traders
Here are the deeper reasons why monitoring employment statistics is essential:
Volatility Anticipation
Employment reports often trigger sharp price swings due to sudden shifts in economic expectations. Traders who track the calendar can prepare stop-loss levels, manage risk, and time their market entries.
Understanding Market Expectations
Each employment release comes with a market consensus forecast. Deviations from expectations – known as surprises – are what typically generate large moves in the forex market. Monitoring forecasts helps traders interpret whether the USD is likely to strengthen or weaken.
Identifying Fundamental Trends
Consistent improvement or deterioration in employment numbers helps traders form long-term biases on U.S. economic performance. This can influence swing trading and long-term positioning, especially when anticipating changes in Federal Reserve policy.
Gauge for Risk Sentiment
Strong employment data usually boosts global risk appetite, while weak data can create risk-off behavior. This affects not only currency pairs but also commodities like Gold, Bitcoin, and equity indices such as the S&P 500 and Nasdaq 100.
Monitoring Fed Policy Signals
Central bankers, particularly the Federal Reserve, heavily rely on employment metrics to set the direction of interest rates. Following the economic calendar allows traders to align their strategy with potential policy shifts.
How Traders Should Use the Economic Calendar Effectively
To use employment releases more strategically, traders should:
- Mark high-impact events (typically flagged in red on most calendars).
- Study the forecast vs. previous data to gauge market expectations.
- Monitor correlated markets (Treasury yields, DXY, equities) before the release.
- Use caution when placing trades minutes before or after data announcements.
- Wait for confirmation candles and post-news market structure before entering positions.
By consistently tracking employment indicators through the economic calendar, forex traders can enhance their understanding of USD strength, global macro conditions, and the broader risk landscape – allowing for more confident and informed trading decisions.
Additional Insights: Price Behavior During NFP & Practical Trading Strategies
Typical Market Reaction Patterns During NFP Releases
The Non-Farm Payrolls report is famous for causing sudden volatility across USD pairs. The table below summarizes common market reactions based on whether the data comes out better, worse, or in line with expectations.
| NFP Result vs Forecast | Market Reaction (Typical) | Impact on USD | Impact on Gold (XAU/USD) | Trader Sentiment |
| Better-than-expected (e.g., higher job creation) | Risk-on moves in equities; stronger Treasury yields | Usually strengthens | Usually falls due to USD strength | Positive for USD; bearish for safe havens |
| Worse-than-expected | Risk-off behavior; increased volatility | Usually weakens | Typically rises | Fear of slowdown; bullish for safe havens |
| In line with forecast | Moderate movement or fake-outs | Neutral or slightly volatile | Mixed reactions | Market often waits for AHE or unemployment rate confirmation |
Real Examples of Market Movement During Previous NFP Events
Below are simplified examples illustrating how major forex pairs reacted during historical NFP releases.
Example 1: EUR/USD Reaction
- Forecast: 200k jobs
- Actual: 270k jobs (significantly higher)
- Immediate reaction:
- EUR/USD drops sharply as USD strengthens
- 40–70 pip drop within the first minute
- Follow-through behavior:
- Price consolidates
- Trend continues downward for 1–3 hours
Example 2: Gold (XAU/USD) Reaction
- Forecast: 190k jobs
- Actual: 150k jobs (weaker data)
- Immediate reaction:
- Gold spikes up aggressively
- 80–120 pip surge (or $8–$12 in Gold pricing)
- Follow-through:
- Volatility remains high
- Price forms a new intraday support zone
Example 3: USD/JPY Reaction
- Forecast: 180k jobs
- Actual: 180k jobs (exactly in line)
- Immediate reaction:
- Mixed wicks (whipsaw) both up and down
- Range-bound movement for 5–15 minutes
- Later reaction:
- Market shifts based on Average Hourly Earnings rather than NFP itself
NFP Trading Strategies: Entry & Exit Approaches for Forex Traders
Because NFP causes extreme volatility, traders need structured trading plans to avoid unnecessary risks. Below are three common strategies used by professional traders—including risk-focused approaches suitable for beginners.
1. The “Wait-and-Confirm” Strategy (Safest for Beginners)
How it works:
- Do NOT enter during the first spike (first 1–5 minutes).
- Allow the initial volatility to settle.
- Wait for a clear direction (breakout + retest).
Entry Rules:
- Enter only after a breakout candle closes beyond a key level (support/resistance).
- Enter on the retest with confirmation from momentum indicators.
Exit Rules:
- Take profit on the next significant support/resistance zone.
- Use tight stop-loss because post-news reversals can be aggressive.
Why it works:
It avoids whipsaws and fakeouts common during the initial release.
2. Straddle Strategy (Advanced Traders)
Setup Before the Release:
- Place a Buy Stop above resistance.
- Place a Sell Stop below support.
- Cancel the opposite order once one of them triggers.
Exit Rules:
- Close partial profit at +30 to +50 pips (depending on the pair).
- Trail the stop-loss using new pullback structures.
Why it works:
It captures the breakout direction regardless of the data outcome.
Warning:
This strategy is high-risk during spreads widening. Only use with experience and proper risk management.
3. Fading the Initial Move (Contrarian Approach)
How it works:
- If price spikes too far too fast, wait for exhaustion.
- Enter in the opposite direction of the initial move.
Signals for Entry:
- Long wicks (rejection candles)
- Divergence on RSI or MACD
- Price failing to hold above/below the spike level
Exit Rules:
- Aim for 20–40 pips depending on volatility
- Stop-loss above the wick high (if selling) or wick low (if buying)
Why it works:
Markets often overreact to the first data release, then normalize.
Risk-Management Tips for NFP Trading
- Use smallest possible lot size due to extreme volatility.
- Expect spreads to widen before and after the release.
- Avoid stacking multiple positions; focus on a single structured trade.
- Never trade NFP without stop-loss—moves can exceed 100–150 pips instantly.
- Backtest your approach across multiple NFP releases.
Further Reading for Forex Traders
- Monitor interest rate decisions using the Central Bank Calendar
- Learn more about NFP and Forex: What is NFP and How to Trade It
Explore our guide on How Interest Rates Affect Forex Markets