Why Forex Risk Management Matters in Currency Trading
Effective forex risk management enables currency traders to limit losses arising from exchange rate fluctuations. More importantly, it creates a structured trading environment that feels safer, more controlled, and significantly less stressful. Without a clear risk management framework, even the most accurate trading strategy can fail over time.
In this guide, we will walk through the fundamental principles of forex risk management and explain how traders can integrate them into a disciplined and sustainable trading process.
What Is Forex Risk Management?
Forex risk management refers to a set of deliberate actions and rules that traders apply to protect their capital from excessive downside exposure. In trading, higher risk can indeed lead to higher potential returns—but it also increases the probability of substantial losses.
The core objective of risk management is not to avoid losses entirely, but to control them, ensuring that no single trade—or sequence of trades—can significantly damage the trading account. Mastering this balance between risk and reward is one of the most critical skills every trader must develop.
In practice, forex risk management involves determining appropriate position size, setting predefined stop losses, and maintaining emotional discipline during trade execution. When applied consistently, these measures often mark the difference between long-term profitability and account failure.
The Five Core Principles of Forex Risk Management
1. Understanding Your Risk Appetite
Defining your appetite for risk is the foundation of effective forex risk management. Traders must ask a fundamental question before entering any position: How much am I willing to lose on this trade?
This consideration becomes especially important when trading highly volatile currency pairs, such as certain emerging market currencies. Liquidity in forex trading also plays a role, as less liquid pairs may make it difficult to enter or exit positions at desired price levels, increasing execution risk.
Without a clear understanding of acceptable loss, position sizes can become excessive, leading to losses that impair both capital and psychological confidence.
From a statistical perspective, even a trader with a 50% win rate will inevitably experience losing streaks. Over a long trading career—say 10,000 trades—the probability of encountering 10 or more consecutive losses is not just possible, but likely. This reality underscores why traders must be financially and psychologically prepared for unfavorable periods.
As a general guideline, many professional traders risk between 1% and 3% of their account balance per trade. For example, with a $100,000 account, this equates to a risk amount of $1,000 to $3,000 per trade—an approach that supports longevity rather than short-term excitement.
2. Choosing the Correct Position Size
Position sizing determines how much exposure you take in the market and directly impacts both account protection and growth potential. Selecting the correct position size requires calculating stop loss distance, determining risk percentage, and understanding pip value relative to lot size.
When position size is aligned with predefined risk limits, traders can remain emotionally stable regardless of trade outcomes. Poor position sizing, on the other hand, often leads to overexposure and unnecessary emotional stress.
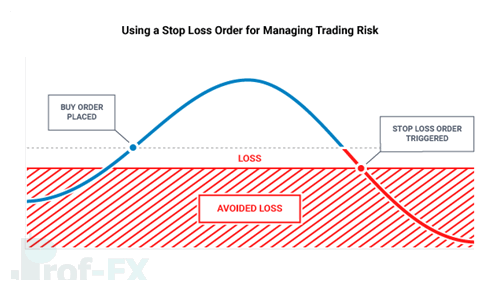
3. Using Stop Loss Orders Effectively
Stop loss orders are one of the most essential tools in forex risk management. These orders automatically close a trade once price reaches a predefined level, preventing losses from escalating beyond acceptable limits.
The placement of a stop loss should be based on market structure and technical reasoning—specifically, the price level at which the original trading idea becomes invalid. Defining this exit point before entering a trade allows traders to act objectively rather than emotionally.
In addition to stop losses, traders should use profit targets to enforce a favorable risk-to-reward ratio, ideally 1:1 or higher. A 1:1 ratio means risking one dollar to potentially earn one dollar, while higher ratios further tilt probabilities in the trader’s favor.
The impact of risk-reward ratios becomes clear when comparing outcomes:
| Risk-Reward | 1:1 | 1:2 |
| Total Trades | 10 | 10 |
| Win Rate | 40% | 40% |
| Profit Target | 100 pips | 200 pips |
| Stop Loss | 100 pips | 100 pips |
| Pips Won | 400 | 800 |
| Pips Lost | 600 | 400 |
| Net Result | -200 pips | +200 pips |
As shown above, a strategy with the same win rate can shift from unprofitable to profitable simply by improving the risk-to-reward ratio. This principle is central to professional trading performance.
4. Managing Leverage Responsibly
Leverage in forex allows traders to gain market exposure beyond the size of their trading account. While this increases profit potential, it also magnifies losses and psychological pressure.
Research conducted by Prof FX Senior Strategist Jeremy Wagner revealed that traders with smaller account balances tend to use significantly higher leverage than traders with larger balances. However, those using lower leverage consistently achieved better results.
Traders using average leverage around 5:1 were profitable far more often than those using leverage above 20:1. This evidence strongly suggests that conservative leverage is a key factor in long-term trading success—especially for beginners.
5. Controlling Emotions in Trading Decisions
Emotional discipline plays a crucial role in managing risk. Emotions such as fear, greed, excitement, or boredom can distort judgment and lead to unnecessary exposure.
One effective way to reduce emotional interference is by maintaining a forex trading journal. By documenting trades, traders can analyze performance objectively, refine strategies based on data, and avoid repeating emotionally driven mistakes.
Forex Risk Management in Practice: A Case Study
Prof FX analyst Nick Cawley provides a real-world example of disciplined forex risk management using a trade on EUR/USD:
“I entered a long position on EUR/USD at 1.1100 with a 1:3 risk-to-reward ratio. My position size was £5 per pip, representing only 3% of my account balance. If the target was reached, the trade would generate £300 in profit.
To manage risk, I placed a stop loss 20 pips below entry, as any move beyond that level would invalidate my trade idea. I used 1:1 leverage and recorded the trade in my journal. This process allowed me to manage risk objectively and minimize emotional involvement.”
This example highlights how predefined rules, proper sizing, and documentation work together to create a disciplined trading environment.
Key Takeaways for Forex Risk Management
To practice effective forex risk management, traders should:
- Clearly define their risk appetite and risk-to-reward ratio
- Use appropriate position sizing based on account balance
- Always place stop losses to limit downside risk
- Avoid excessive leverage
- Actively manage emotions through structure and discipline
- Maintain a trading journal to support data-driven decisions
Further Learning for Forex Traders
For traders new to the forex market, our New to Forex Trading Guide offers a comprehensive introduction to the world’s largest financial market. Traders of all experience levels can also follow real-time insights in our Analyst Picks section to see how professionals apply risk management principles in live market conditions.