The forces of supply and demand are the most fundamental drivers of price in any capitalist system. Much like the laws of gravity, these forces operate continuously and invisibly, shaping market behavior whether traders recognize them or not. In every financial market, buyers and sellers engage in a constant negotiation, pushing price toward a level where both sides temporarily agree.
Although traders often search for complex explanations behind price fluctuations on a chart, the underlying cause of all price movement ultimately comes down to one simple relationship: the balance between supply and demand.
In general terms, positive economic or financial news tends to increase demand while reducing supply, leading to higher prices. Negative news typically has the opposite effect—demand weakens, supply increases, and prices fall.
In this article, I will walk you through the foundational concepts behind supply and demand and explain how these forces operate in the forex market.
This guide covers:
- What supply and demand really mean
- Supply and demand zones explained
- How supply and demand function in the forex market
- How supply and demand influence price movements
What Does Supply and Demand Mean in Trading?
Supply and demand describe the relationship between buyers and sellers and form the basis of price determination in financial markets. Price moves as the market attempts to find an equilibrium, a level where the quantity buyers are willing to purchase equals the quantity sellers are willing to offer.
When demand exceeds supply, price rises. When supply outweighs demand, price falls. This continuous interaction creates the price fluctuations traders observe on forex charts every day.
The Laws of Supply and Demand Explained
In simple terms:
- Supply refers to how much of an asset is available for sale.
- Demand refers to how much of that asset buyers are willing to purchase.
These two forces respond directly to price changes and economic incentives. Their interaction is often illustrated through economic curves that show how quantity and price relate to one another.
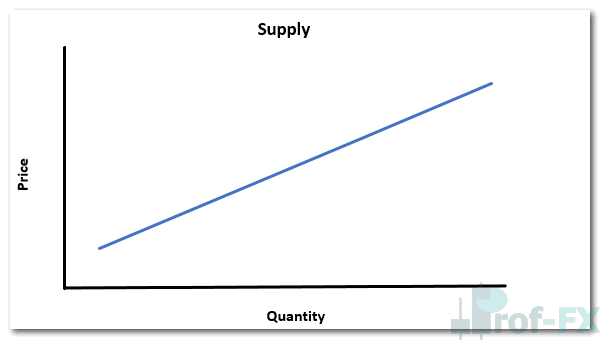
Supply: Price vs Quantity Relationship
As price increases, sellers are generally more willing to supply more of an asset to the market.
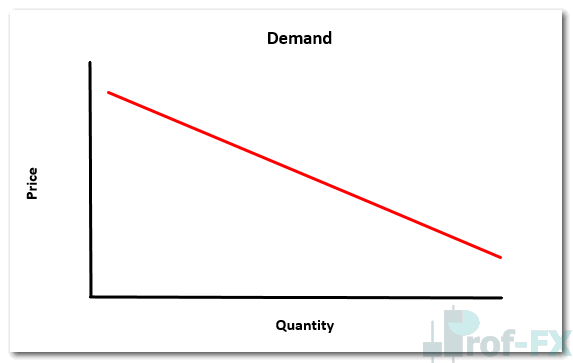
Demand: Price vs Quantity Relationship
As price decreases, buyers typically demand more of the asset because it appears cheaper or more attractive.
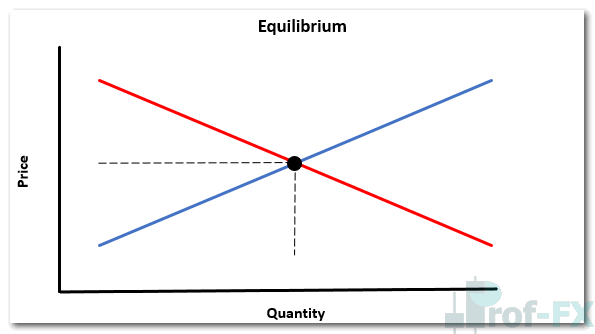
Equilibrium: Where Supply Meets Demand
The equilibrium price represents the most efficient market level—where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded. At this point, neither buyers nor sellers have a strong incentive to push price higher or lower.
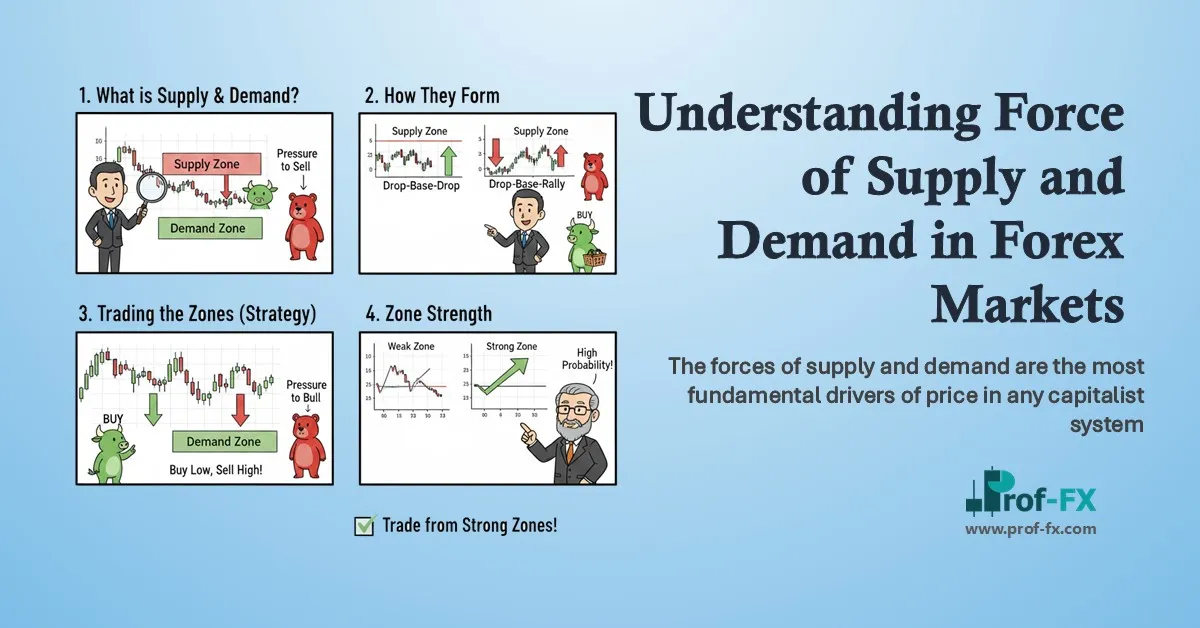
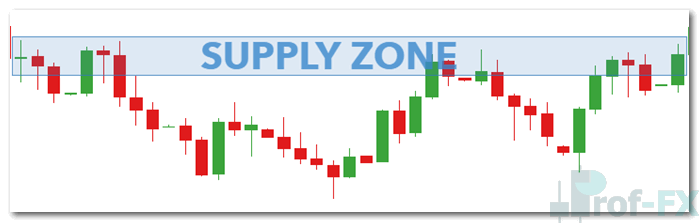
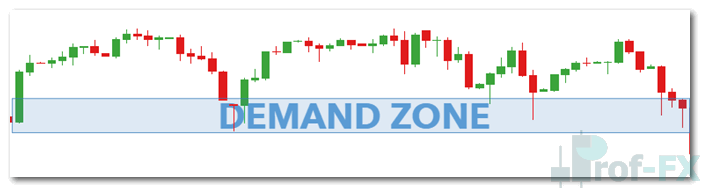
Understanding Supply and Demand Zones
Supply and demand zones give traders a practical way to visualize these forces directly on a price chart. Instead of focusing on a single price level, zones represent broader areas where buying or selling pressure has repeatedly entered the market.
Unlike traditional support and resistance—which are often drawn as thin horizontal lines—supply and demand zones cover wider price regions. This makes them more realistic and reliable, as market participants rarely react at an exact price.
A supply zone forms where sellers consistently overwhelm buyers, causing price to drop sharply. A demand zone forms where buyers aggressively step in, pushing price higher. These zones often generate fast and decisive price movements, reflecting strong institutional participation.
For traders looking to deepen their understanding, learning the core trading principles behind supply and demand can significantly improve chart analysis skills.
Supply and Demand in the Forex Market
The dynamics of supply and demand in the forex market are not fundamentally different from those in a simple vegetable market. The main difference lies in speed, scale, and complexity.
The forex market is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, driven by constant demand for currencies. Because currencies underpin global trade, investment, and capital flows, every international transaction involving different economies requires currency exchange.
Central banks, commercial banks, hedge funds, multinational corporations, and retail traders all contribute to supply and demand in the forex market. The combined actions of these participants create continuous price movement across multiple time frames.
How Supply and Demand Influence Forex Prices
At its core, supply and demand analysis involves assessing the relative number of buyers and sellers in the market at any given time.
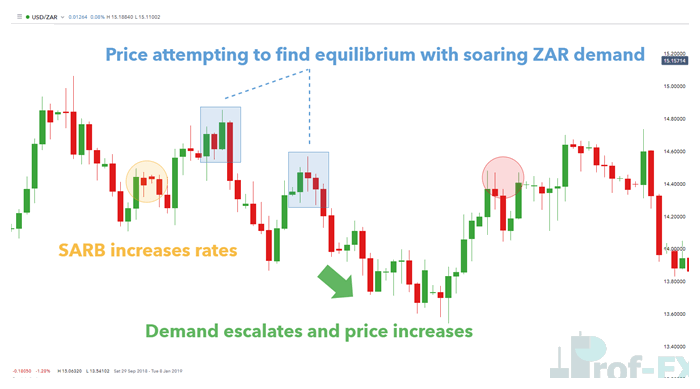
A Practical Example: Interest Rates and Supply–Demand Shifts
Consider a scenario where the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) raises interest rates. This decision triggers a chain reaction driven by supply and demand forces.
When interest rates rise, forex rollover payments—also known as swap rates—increase. Traders holding positions past the rollover time may receive higher interest income for holding certain currency pairs.
This creates a clear incentive:
- More traders are encouraged to buy the higher-yielding currency.
- Fewer traders are willing to sell it, as the opportunity cost of selling has increased.
As demand rises and supply falls, price moves higher to reflect this imbalance.
Supply and demand in action – USD/ZAR daily chart:
As price climbs, it eventually reaches a level where buyers are no longer willing to pay higher prices. At that point, sellers begin to dominate, causing price to decline.
Once price falls far enough, buyers return—remembering the higher interest rate and rollover advantage. This lower price represents perceived value, attracting renewed demand and pushing price higher once again.
This continuous process reflects how markets seek fair value, unfolding across all time frames and across every financial market worldwide.
For traders who want a deeper dive, an in-depth guide to trading supply and demand can provide further clarity and practical examples.
Combining Supply and Demand with Support and Resistance
Supply and demand work closely alongside support and resistance. When price breaks through key support or resistance levels, it often signals a shift in supply and demand dynamics within that currency pair.
Understanding how these concepts interact allows traders to better anticipate potential breakouts, reversals, and trend continuations.
To explore this relationship further, traders can study how supply and demand compare with traditional support and resistance techniques and how professionals combine them effectively.