Why Forex Traders Must Monitor Both Monetary and Fiscal Policy
When trading the financial markets – especially during periods of heightened uncertainty or fears of a global economic slowdown – it is essential for traders to closely monitor both government fiscal policy and central bank monetary policy.
These two policy forces act as the primary levers of economic stabilization. When they work in alignment, the likelihood that an economic slowdown escalates into a full-scale recession is significantly reduced. However, when monetary and fiscal policy move in opposing directions, the risk of financial instability and market dislocation increases dramatically.
For forex traders, understanding this interaction is not optional—it is a core macroeconomic skill that directly affects currency valuations, capital flows, and market sentiment.
Why Monetary and Fiscal Policy Matter During Economic Downturns
Trading during periods of weak economic conditions requires a more disciplined macroeconomic approach. In times when growth is slowing and recession risks are rising, monitoring both central bank actions and government fiscal decisions becomes more important than ever.
This is because the right combination of policy responses can prevent a crisis and accelerate recovery, while poorly coordinated or mistimed policies can accelerate market collapse and deepen economic pain.
From a trader’s perspective, policy decisions often determine whether markets stabilize, trend strongly, or experience sharp volatility—particularly in forex pairs linked to major economies such as the United States, Eurozone, Japan, and China.
Understanding the Difference Between Monetary and Fiscal Policy
At a fundamental level, the distinction is straightforward:
- Fiscal policy refers to a government’s decisions on taxation, public spending, budget deficits, and debt issuance.
- Monetary policy refers to a central bank’s control over interest rates, liquidity, money supply, and credit conditions.
While these policies operate through different channels, they are most effective when they support each other. Conversely, they become far less effective—and sometimes counterproductive—when they are pulling the economy in opposite directions.
For example, aggressive government spending may fail to stimulate growth if a central bank maintains tight monetary conditions due to inflation concerns.
The Importance of Monetary and Fiscal Policy Coordination
Independence of Central Banks in Advanced Economies
In many developed economies—such as the United States, United Kingdom, and Eurozone—central banks operate independently from governments. This independence is designed to protect monetary policy from short-term political pressure.
However, this structure can also create policy friction. For instance, tax cuts or fiscal stimulus may boost growth expectations, but their impact can be muted if a central bank refuses to loosen monetary policy out of fear of rising inflation or asset bubbles.
This lack of coordination can dilute the effectiveness of both policy tools.
Case Studies: Global Approaches to Policy Coordination
Japan and the “Three Arrows” Strategy
Japan offers a notable example of partial coordination. Although the Bank of Japan (BoJ) gained greater independence from the Ministry of Finance in 1997, political influence has remained significant.
Under former Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, Japan implemented the well-known “Three Arrows” policy, which combined:
- Aggressive monetary easing,
- Expansionary fiscal policy,
- Structural reforms aimed at boosting private investment.
This approach highlighted how coordinated policy can influence long-term market expectations, particularly in JPY currency pairs. Japan’s close relationship between government, banks, and corporations—often referred to as “Japan Inc.”—has also shaped investor perceptions for decades.
Emerging Markets and Political Pressure on Central Banks
In countries such as India and Turkey, central banks often face strong political pressure to align monetary policy with government fiscal goals. This can increase market volatility, as traders question the credibility and independence of monetary authorities.
Interestingly, in China, the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) maintains limited operational independence despite ultimate control by the Communist Party. Several Asian economies openly coordinate fiscal and monetary policy, which can lead to decisive—but sometimes opaque—market outcomes.
Political Influence and Monetary Policy in the United States
In the United States, tensions between fiscal and monetary authorities have also been evident. Former President Donald Trump repeatedly criticized the Federal Reserve, urging it to cut interest rates to support growth and counter China’s monetary easing.
In a May 2019 tweet, Trump argued that if the Federal Reserve matched China’s stimulus measures, the U.S. would gain a decisive economic advantage. While his comments were widely criticized, they highlighted a key reality: major global economies actively use monetary policy as a competitive tool.
For forex traders, such public disputes can signal future policy shifts and increased volatility in USD-based currency pairs.
Trading Financial Markets When Central Banks Run Out of Options
From a short-term trading perspective, central banks exert the most immediate influence on market prices. Interest rate decisions, forward guidance, liquidity injections, and unconventional monetary tools often trigger instant reactions in forex, equity, and bond markets.
Government fiscal measures—such as tax reforms or infrastructure spending—tend to have a longer-term impact and may be offset by central banks if inflation risks rise.
However, when interest rates approach zero or turn negative, monetary policy reaches its limits, and fiscal policy becomes increasingly important.
Unconventional Policy Tools in a Low-Rate World
In recent years, major economies have introduced increasingly complex policy tools to support growth:
- Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP)
Introduced by the U.S. in 2008 during the subprime mortgage crisis, TARP involved purchasing distressed assets and equity from financial institutions. - Term Asset-Backed Securities Loan Facility (TALF)
Created by the Federal Reserve in 2008, TALF is a clear example of coordinated fiscal and monetary policy working toward the same objective. - Quantitative Easing (QE)
Central bank purchases of government and private securities to expand the money supply and encourage lending and spending. - Quantitative and Qualitative Monetary Easing (QQE) with Yield Curve Control
Implemented by the Bank of Japan in 2016 after traditional QE failed to generate sufficient inflation. - Targeted Longer-Term Refinancing Operations (TLTROs)
Introduced by the European Central Bank (ECB) to provide low-cost, long-term funding to banks and stimulate credit creation in the real economy.
How Policy Announcements Impact the Forex Market
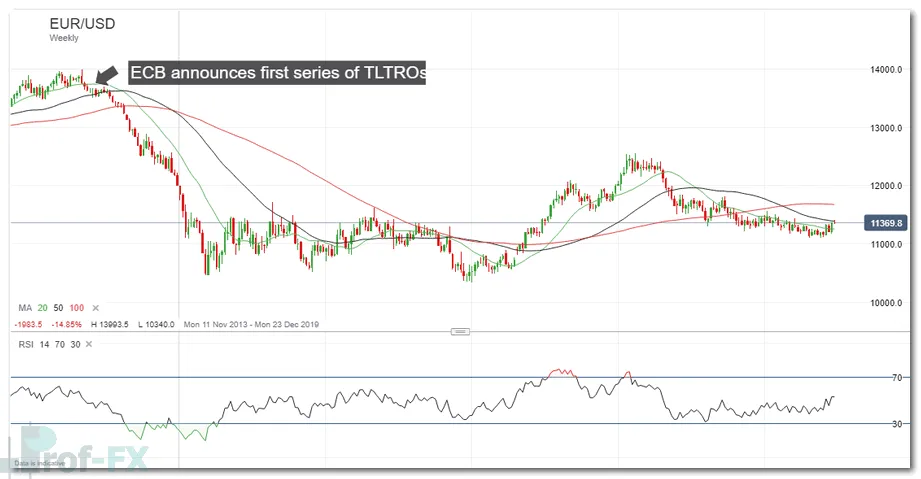
The impact of these measures is clearly visible in currency markets. For example, the ECB’s announcement of the first TLTRO program in June 2014 triggered a prolonged decline in EURUSD, as expectations of looser monetary conditions weighed on the euro.
EURUSD Price Chart, Weekly Timeframe (November 11, 2013 – June 27, 2019)
This illustrates a critical lesson for traders: policy expectations often matter as much as policy actions themselves.
Key Lessons for Forex Traders
The takeaway for traders—especially beginners—is clear. Both governments and central banks shape financial markets, but they do so in different ways and over different time horizons.
Monitoring policy announcements, economic data, and political developments is essential—particularly when fears of a global slowdown or recession are rising. In such environments, macroeconomic awareness can be the difference between informed trading decisions and costly mistakes.
Resources to Help You Trade the Forex Markets
Whether you are new to forex trading or looking to refine your skills, platforms like Prof FX offer valuable educational tools, including:
- Analytical and educational webinars hosted multiple times per day
- In-depth trading guides designed to improve performance
- Beginner-focused forex education resources
- Expert insights into trader psychology through guides such as Traits of Successful Traders
Building a strong foundation in monetary and fiscal policy analysis will not only improve your understanding of the markets—it will help you trade with greater confidence and discipline over the long term.